Even though all body fat is generally referred to as “fat,” there are different types of body fat. Some fats can harm your health and increase the risk of disease. Others are advantageous and required for your wellness.
Table of Contents
Related Readings
Vegan Diet for Belly Fat Loss
Low Cholesterol Protein Powders
For the majority of us, being fat is considered terrible. Scientists have found that fat is one of the most amazing organs in the body because it does so many different things.
The body gets its energy from stored fat, so everyone needs body fat to survive. Fat also protects some organs from getting too hot and is a cushion. Your body benefits from having the proper type of fat.
However, you may be at risk of several major health problems if your body doesn’t have the proper balance of different types of fat.
What Is Body Fat?
The word “body fat” refers to the fat cells that live inside the human body. The main job of these cells is to store energy until the body needs it.
This energy comes from the nutrients in food. The body’s insulation is its secondary function.
Most of the body’s fat is under the skin, but some types of body fat can also be found around internal organs, where they protect them.
Types of Body Fat
Three main types of body fat cells can be stored in three different ways. White, brown, or beige fat cells can be stored as vital, subcutaneous, or visceral.

Each type of fat has a varied function; some promote a healthy metabolism and hormone levels, while others lead to chronic diseases, including diabetes, heart disease, cancer, and hypertension, that are life-threatening.
While there are other approaches to analyzing body fat, evaluating what’s mostly good and bad for your general health is easiest.
Brown Fat
Brown fat is mostly in charge of keeping the body at the right temperature and burning energy. Brown fat is simple to burn because it isn’t stored fat, which makes it particularly useful in colder climates.
Managing brown fat isn’t necessary as long as you keep your levels of essential fats up to help healthy brown fat form.
Brown fat increases subcutaneous fat relative to visceral fat, lowering the risk of diabetes and fatty liver disease. White fat distribution improves with brown fat.
Essential Fat
It is considered very good for the body.
Essential fat has the most suitable name and is necessary for optimal health. It controls the production of reproductive hormones, the body’s temperature, and the absorption of vitamins, among other important things. Although it is spread throughout the body, essential fat is not readily apparent.
Because essential fat is “healthy” fat, it is not the sort you should aim for when trying to lose weight. According to the American Council on Exercise, the recommended necessary fat range for females is between 10–12%, whereas, for males, the range should be between 2-4%. Extreme, unhealthy exercise and dieting usually result in essential fat loss.
White Fat
It is considered both good and bad for your health.
It is the body’s main source of energy storage. As a source of leptin, white fat is important for controlling insulin to keep blood sugar levels stable. Because it makes leptin, it also helps control hunger. This is because it produces the hormone adiponectin. The regulation of cortisol and growth hormones is also aided by white fat. White fat can be helpful in normal amounts, but too much is bad. Increased white fat can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of weight gain and related health issues.
One of the main indicators of higher levels of white fat is stubborn excess fat on the thighs, hips, and abdomen. Workouts that focus on building muscle, which burns more calories than fat, can aid in lowering the body’s white fat levels.
Beige Fat
It is considered good for the body.
Beige fat cells are between white and brown. When body temperature drops, they burn energy like brown fat cells. Cold temperatures and neurological and immunological systems aid browning.
Cold exposure increases human beige and brown fat activity, negatively related to age, body mass index, and circulating lipid and glucose levels.
Stress causes the body to produce beige fat, which causes white fat to become beige. While having a high level of beige fat isn’t a goal, it is a step toward having healthy levels of excellent brown fat. It allows bad fat to be changed and burned as heat energy to keep the body’s core temperature steady.
It is a beneficial fat to target for weight loss because beige fat converts white fat into useful thermal energy. Due to the release of the hormone irisin, exercise is thought to be an important stressor for converting white fat to beige fat. Since stress is the main factor, aim for at least 75 minutes of physical activity per week and favor high-intensity interval training to raise irisin levels that cause white fat to “beige.”
Visceral Fat
Visceral fat is the white fat found in the abdomen and between organs. It is considered bad for the body. It builds up and releases retinol-binding protein 4, a known cause of insulin resistance. Visceral fat has also been linked to a higher risk of Alzheimer’s disease, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, stroke, and dementia. Age normally causes an increase in visceral fat levels.
Dietary changes are among the best approaches to reducing visceral fat levels. Lean proteins (chicken, eggs, beans), various types of unsaturated fats (fish, nuts, avocados), whole grains, and fiber should replace processed foods in your diet (beans, berries, oatmeal). Getting better sleep habits will also help you lose weight; the recommended range is seven to nine hours. Also, compared to cardio, some abdominal strength-training routines will help you burn more calories and eliminate visceral fat than cardio.
Subcutaneous Fat
It is considered both good and bad for the body.
About 90% of the body fat comprises subcutaneous fat beneath the skin. Estrogen is made in subcutaneous fat, which often builds up as stubborn fat on a woman’s thighs or around a man’s stomach. Women often have more subcutaneous fat because estrogen has a bigger impact on female fertility. This particular form of fat also serves as a barrier and cushion layer between muscle and skin tissue.
Subcutaneous fat is important, but having too much of it could make health problems more likely, especially in the area around the abdomen. Subcutaneous fat is the hardest to eliminate because your body stores it as a safety net in case you get hungry or don’t eat enough. Over time, extra subcutaneous fat can be lost by cutting back on calories, focusing more on better nutrition by avoiding processed foods and refined carbohydrates and frequently exercising at a high intensity. In contrast, when paired with a healthy diet and regular exercise, radio frequency-based body shaping treatments may further aid in targeting and reducing fat cells more rapidly.
What Is a Healthy Body Fat Percentage?
Our society has portrayed “fat” as the enemy of good health and nutrition. However, the truth is that the human body needs fat. Fat not only keeps us warm, but it also helps us digest the nutrients in our food. But how much fat is the ideal quantity?
For a man, 2–5% fat is essential, 2–24% is considered healthy, and more than 25% classifies as obesity. For a woman, 10–13% fat is essential, 10–31% is healthy, and more than 32% are classified as obese.
The body mass index, or BMI, has traditionally been used to estimate the body fat percentage. However, calculating someone’s BMI does not calculate their true body fat percentage. An MRI or CT scan is the most accurate approach to determining body fat percentage, but these procedures are too expensive and invasive to be recommended only for this purpose. A person’s body fat percentage is commonly calculated using a calculation that considers their age, weight, gender, and height. Some online calculators let you enter data to calculate your body fat percentage.
The amount of healthy body fat varies from person to person and relies on several variables. Instead, guidelines have been set for how to evaluate men and women of different ages and fitness levels.
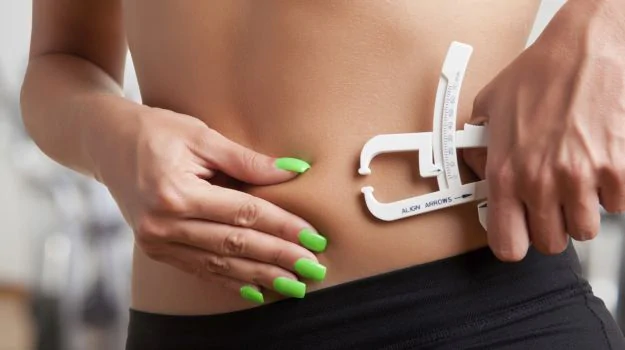
Body fat percentage and BMI continue to have a strong relationship. Since body fat cannot be seen, using calipers to measure BMI is a useful way to obtain a sense of what is happening inside the human body. Having this done by a medical expert is the best way to ensure precise findings.
Even though BMI is frequently a good predictor of body fat percentage, keep the following in mind:
- Despite having the same BMI, women naturally have a higher body fat percentage than men.
- Even though they have the same BMI, older adults naturally have a larger body fat percentage than younger adults.
- Compared to non-athletes, athletes typically have lower percentages of body fat.
- Different ethnic groups naturally have different percentages of healthy body fat.
Conclusion
A healthy, functional body requires essential fat. Most of our body’s fat is subcutaneous and beneath the skin. The body uses this technique to store energy for later use.
In the abdomen, around the major organs, is where you’ll find visceral fat. When levels are high, it can be extremely harmful. You run a higher risk of contracting several diseases if you have a high body fat percentage, especially visceral fat.
Aditi Paul Chakraborty is a food and wellness writer. She is a double postgraduate in English Literature and Mass Communication and Journalism from MIT and a regular at various international film festivals.
She is a movie buff, a painter, a traveler, and a shopaholic. She is happily married to a loving husband and has a caring mother-in-law.